
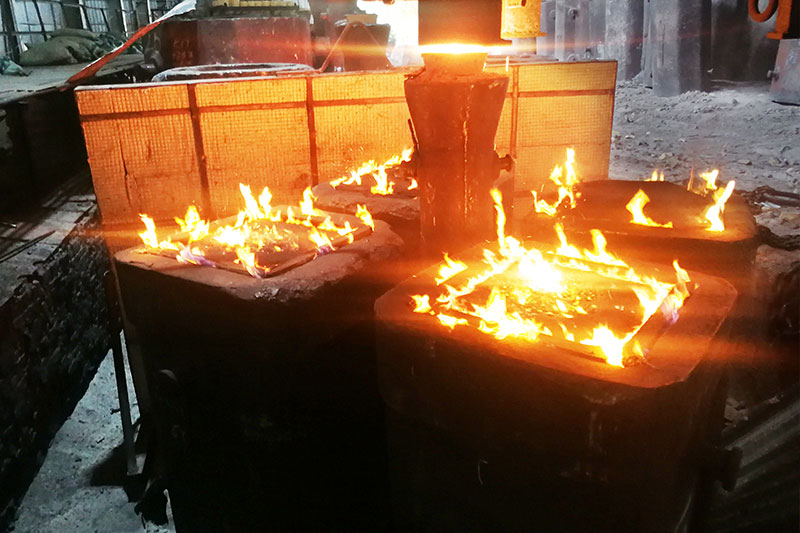
At present, in order to make use of the waste heat of large forgings, after forging, the heat of the parts is directly used for heat treatment. There are generally three types of forging waste heat heat treatment. Next, I will explain these three types in detail:
(1) After forging heat treatment of forging parts: that is, the forging parts are directly subjected to heat treatment after forging, which closely combines forging and heat treatment. This process is also called high temperature deformation heat treatment. After forging heat treatment can save a lot of energy and man-hours, and improve labor Productivity, in addition, cross heat treatment can also make forgings to obtain good comprehensive mechanical properties. For this reason, countries all over the world adopt a large amount of post-forging waste heat treatment: that is, by controlling the forging and controlling the after forging, to prevent the formation of coarse ferrite and pearlite as well as the precipitation of two-shaped carbides, so that it can directly obtain the equivalent of forging again. The structure and performance of conventional normalizing, isothermal normalizing and quenching performed by heating. In this way, conventional normalizing, equal overflow E hardening and reheating of quenching can be cancelled.
(2) After forging heat treatment of forged parts: that is, the forging parts after forging are directly sent to the average temperature heat treatment process, and the heat treatment process is still performed according to the conventional forging heat treatment process. This method is called waste heat homogenization heat treatment, such as a PSH type 63MN electric The screw press forging automatic production line is equipped with an automatic quenching and tempering line of a 270kW suspension temperature quenching electric furnace. If the residual heat of the forging is not used, it is necessary to be equipped with a 1000kW quenching resistance heating furnace to produce light vehicle crankshafts and front axles .
(3) Then use part of the waste heat for heat treatment: that is, after inlaying waste heat quenching, after forging, both through waste heat quenching, after forging waste heat normalizing and after forging waste heat isothermal normalizing, the grain size of forgings is larger than conventional heat treatment, which is refined The grain can cool the forging to 600C~650C, and then heat the forging to the required temperature for quenching (normalizing) for quenching (normalizing), which can refine the grain and save the forging from room temperature to 600C. ~650C energy consumption, generally used for forgings with high grain size requirements, which can save about 60% of energy
Megosztás a facebookon
Forging refers to a workpiece or blank obtained by forging and deforming a metal blank. By applying pressure to the metal blank, it produces plastic deformation, which can change its mechanical properties. According to the temperature of the blank during processing, forgings can be divided into cold forging and warm forging and hot forging. Cold forging is generally processed at room temperature, and hot forging is processed at a temperature higher than the recrystallization temperature of the metal blank.
The preparation before forging includes raw material selection, calculation, blanking, heating, calculation of deformation force, selection of equipment, and design of molds. It is necessary to choose a good lubrication method and lubricant before forging.
Forging materials involve a wide range, including steel and high-temperature alloys of various grades, as well as non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, titanium, copper, etc.; there are both bars and profiles processed into different sizes at one time, and a variety of Ingots with specifications; in addition to using a large number of domestic materials suitable for my country's resources, there are also materials from abroad.
Forging
Most of the forged materials are listed in national standards, and many are new materials developed, tried and promoted. As we all know, the quality of products is often closely related to the quality of raw materials. Therefore, for forging workers, they must have the necessary material knowledge and be good at selecting the most suitable materials according to the process requirements.
Material calculation and blanking are one of the important links to improve material utilization and realize blank refinement. Too much material not only causes waste, but also aggravates cavity wear and energy consumption. If the blanking does not leave a margin, it will increase the difficulty of process adjustment and increase the scrap rate. In addition, the quality of the blanking end face also has an impact on the process and the quality of cylindrical forgings.
The purpose of heating is to reduce forging deformation force and improve metal plasticity. But heating also brings a series of problems, such as oxidation, decarburization, overheating and overburning. Accurate control of the initial forging and final forging temperature has a great influence on the product structure and performance. Flame furnace heating has the advantages of low cost and strong applicability. However, the heating time is long, oxidation and decarburization are prone to occur, and the working conditions need to be continuously improved. Electric induction heating has the advantages of rapid heating and less oxidation, but it has poor adaptability to product shape, size and material changes.
Forging forming is produced under the action of external force. Therefore, correct calculation of deformation force is the basis for selecting equipment and checking mold. The stress and strain analysis inside the deformed body is also indispensable for optimizing the process and controlling the structure and performance of the forging.
There are four main methods for analyzing deformation force. Although the principal stress method is not very strict, it is relatively simple and intuitive. It can calculate the total pressure and the stress distribution on the contact surface of the workpiece and the tool. The slip line method is strict for the plane strain problem. It is relatively intuitive to solve the stress distribution for the local deformation of high parts, but the scope of application is narrow.
Forging
The upper limit method can give an overestimated load, and the upper limit element can also predict the shape change of the workpiece during deformation. The finite element method can not only give the external load and the change of the workpiece shape, but also the internal stress and strain distribution. The disadvantage is that the computer time is more, especially when the elastoplastic finite element is used to solve the problem, the computer capacity is larger. The machine time is longer. Recently, there is a trend to adopt a joint method to analyze problems, for example. The upper limit method is used for rough calculation, and the finite element is used for detailed calculation in key parts.
Reducing friction can not only save energy, but also increase the die life of forgings. Since the deformation is relatively uniform, it helps to improve the structure and performance of the product. One of the important measures to reduce friction is to use lubrication. Due to the different forging methods and the difference in working temperature, the lubricants used are also different. Glass lubricants are mostly used for forging of high-temperature alloys and titanium alloys. For hot forging of steel, water-based graphite is a widely used lubricant. For cold forging, due to the high pressure, phosphate or oxalate treatment is often required before forging.
Megosztás a facebookonIndustry and Information Development Department July 30 Publish-type steel operation business information, 1st half of 2020, steel operation business depreciation, post-development influence, promotion of production/reproduction, production and production, maintenance and maintenance. However, it is important to note that it is important to understand that it is important to understand that it is important to understand the situation.
At the same time, steel material consumption increased. From January to June, the consumption amount of crude steel in Japan was 4,806,600, and the rate of increase was 3.8%. Among them, in June, the country's gross steel surface consumption amount reached 90.31 million, the increase of 8.6%.
Several installations, high-ranking production of steel production in the first half of the year. January-June-June, national raw steel, coarse steel, steel material segregation 4.34.3 billion, 4.99 billion sum 6.06 billion, same fraction increase 2.2%, 1.4% sum 2.7%. Among them, in June, nationwide production of raw iron, coarse steel, and steel materials was classified as 77.64 million to 91.58 million and the amount to 115.85 million was increased by 4.1% and 4.5% to 7.5%.
This place is also a low-order loitering holding steel material. Installed Chinese steel industry industry association monitoring, January to June, China steel material rating index average 101.0 points, down 7.7%. Among them, in June, China Steel Material Rating Index averaged 103.1 points, down 5.4%.
According to the usage of steel industry business information, ratio of Yoichi season, two-season factories local new construction and construction area, train production volume, ship production classification increase 145.8%, 87.1%, 55.9%, potential support completion production increase.
At the same time, the amount of glazed stone head opening increased. TS SERIES Manufacturers

“High-ranking, high-ranking, high-performance, high-efficiency, high-competitive, high-competitive force.” What sentence wave display, negative-movement, national-transaction-improvement-improvement, end-of-life external environment, demand Restoration super-departure period, steel products supply insurance, influential affairs, completion of employment, settlement, epidemiological consideration.
ry-June-July, Gourmet stone cumulative progress, 5469.10 million, same ratio increase of 9.6%; Progress average 90.2 M/M, same ratio increase of 0.9%, comparative seasonal increase of 1.8%. Among them, in June, Yinling Yishinshikou 101.68 million, environmental ratio increase 16.8%, same ratio increase 35.3%.
Megosztás a facebookon
There are some defects in the production process of die steel. This is a very large scale. From a macro perspective, any problems that we show during the production process can be attributed to the defects of sunshine. This time-sharing problem is in the process of processing We must work hard in the middle, we should review the selection of mold structural materials and specific treatment, as well as the processing between each other. We must take this aspect into consideration in a timely manner.

Inspection from scratch
If it is found that the mold steel is defective, we have to do the inspection from the beginning, take a look at the processing of the mold's structural materials and other aspects. We must take into account the specific issues in this regard in time and make some correspondence In order to bring us more assurance, we hope that everyone can better understand this aspect.
Try not to repair
When people find that there is a problem with mold steel, try not to repair it. As such a method damages the image of the company, it will also leave a lot of risks together, so we should be lively when we pay attention to these problems. To consider various situations, and then deal with these aspects of the work, so that other situations can be effectively avoided, so I still hope everyone can understand in time.
Timely replacement
After discovering the defects, we must do the replacement work in time. These are very important to us. Because we can take these aspects into consideration in the process of making replacement work, and The whole replacement work is done very well, and a more suitable mold is found before it can play a good effect, so we should understand these.
Megosztás a facebookonGoing deep into the science, steel forging can be classified into two basic types:
CLOSED DIE FORGING
In the closed die technique, the metal is pressed between two dies that comprises of the precut profile of the desired shape.
OPEN DIE FORGING
In open hot forging steel, the metal piece goes through a deformation between multiple dies that do not enclose the material entirely. The dies constantly hammer the metal to achieve the desired shape.
The bonus of forged steel is that the metal becomes stronger than equivalent types that are cast or machined. Steel forging is commonly used in mechanical and industrial applications due to its strength, availability, and specialized alloy types like stainless steel and carbon steel. Forging in steel offers unsurpassed resilience for manufacturing parts that simply do not fail. The various benefits of forging are:
Steel forge parts offer a higher degree of reliability and tolerance capabilities
Steel forgings offer uniformity of composition and structure. They have minimum variation in machinability and mechanical properties
Forged steel parts are stronger and more reliable than machined or cast parts
Steel forgings make possible designs that accommodate high loads and stresses
Steel forgings are used when quality cannot be questioned
Steel forge parts are free from gas voids, pockets, or cooling defects which can lead to load failure
There are the following 5 types of common plastic mold steel:
1.Corrosion-resistant type
Uses: mainly used in the production of materials such as polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, ABS plus flame-retardant resin, which will decompose corrosive gases.
Grades: Typical grades of corrosion-resistant plastic steels commonly used abroad are martensitic stainless steel and precipitation hardening stainless steel, such as STSAX (4Cr13) and ASSAB~8407 of ASSAB company in Sweden. Common domestic are high-carbon high-chromium corrosion-resistant steels such as 1Cr17Ni2 martensitic stainless acid-resistant steel, 0Cr16Ni4Cu3Nb precipitation hardening stainless steel, etc.
2.Tempering type
The quenched and tempered type refers to the quenching and tempering process after the mold is processed to make the mold performance better. There are three main categories:
Carbon steels such as 45 and 55
Uses: Suitable for molds with simple shapes or low precision requirements and short service life.
40CrMo, 42CrMo.
Uses: the former has good low-temperature impact toughness and low notch sensitivity, suitable for making medium-sized molds; the latter belongs to high-strength steel, and has a high fatigue limit, good low-temperature impact resistance, suitable for manufacturing large size requiring certain strength and toughness , Medium-sized plastic mold.
38CrMoAl, 5CrNiMo.
Uses: The former is suitable for plastic molds of PVC and PC. The latter is mainly used for molds with high temperature and high wear resistance requirements, such as thermosetting plastic molds.
3. Age hardening type
Uses: Age hardening type is mainly used to manufacture high-precision, complex cavity plastic molds, which is expensive. There are two categories of maraging steel and precipitation hardening steel.
Grades: Typical grades are newly developed low-cobalt, cobalt-free, low-nickel maraging steel and MAST maraging steel.
Among them, the low-cobalt, non-cobalt, low nickel maraging steel, the hardness of the tempered steel is about 30HRC, and the hardness after aging treatment can reach 38-42HRC. MAST maraging steel has a hardness of 28-32HRC after solid solution and 48-52HRC after aging. The steel has high toughness, small changes in aging size, and good welding performance.
4. Carburizing type
Uses: Carburized steel has low hardness and good plasticity after annealing, and can be formed by cold extrusion.
Grades: Typical grades are 8416 in Sweden and P2 and P4 in the United States.
Chemical composition: The carburized plastic mold steel has a low carbon content, and the element Cr is often added. At the same time, appropriate amounts of Ni, Mo, V are added to improve the hardenability and carburizing ability. After annealing, the response should be ≤100HBS.
5. Pre-hard type
Uses: The pre-hardened type is a mold steel developed to avoid deformation of large and medium-sized precision molds after heat treatment and to ensure the accuracy and performance of the molds.
Brand: The pre-hardened plastic mold steels listed in the national standard are only 3Cr2Mo (P20) steel and 3Cr2MnNiMo.
Chemical composition: It is pre-conditioned and has a hardness of 30-40HRC. This type of steel is generally low-carbon alloy steel with a carbon content of 0.35%-0.65%. Commonly used alloy elements are Cr, Ni, Mn, V, etc. To improve its machinability, S, Ca, etc. are added.
Megosztás a facebookon